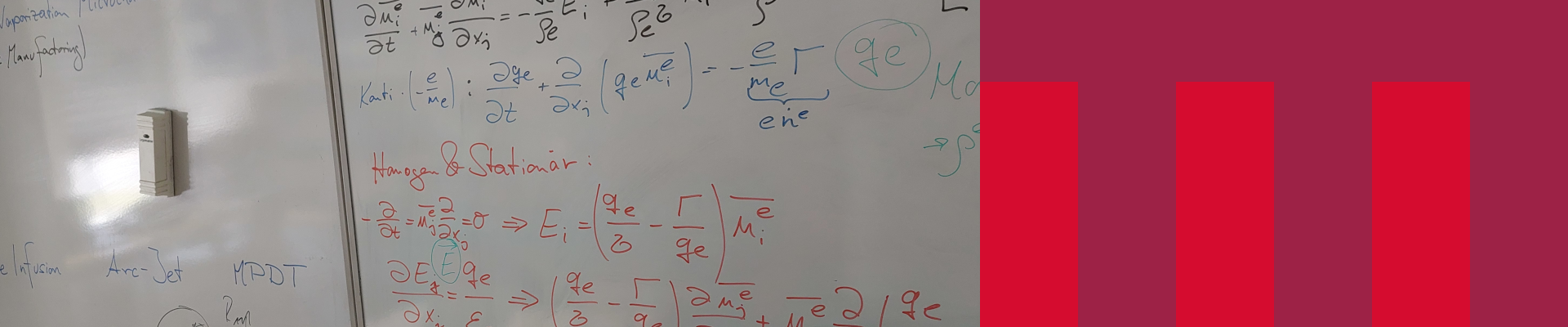
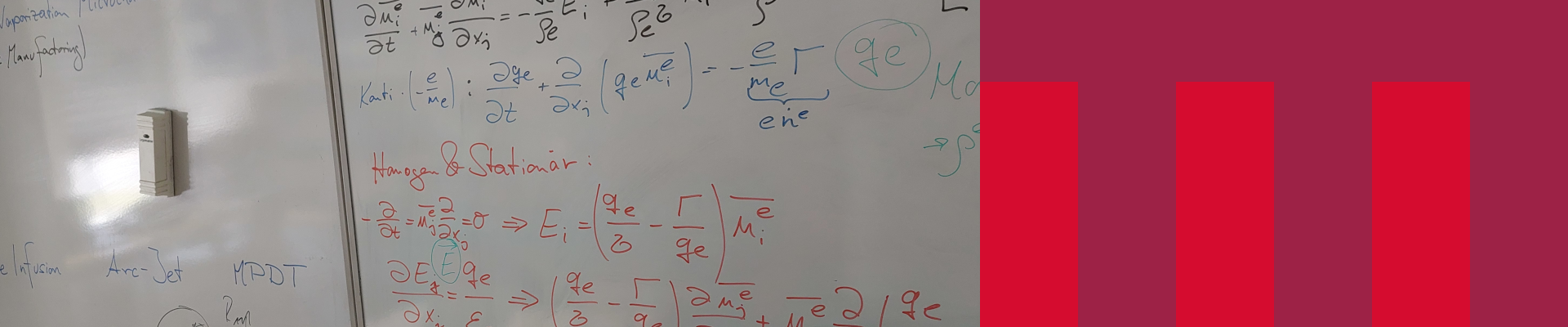
 |
|
Fluid DynamicsProf. Dr.-Ing. R. Groll
Original title Part A: Einführung in die Strömungslehre / Laminare Strömungen (VAK 04-26-KD-002) |
 |
|||
 |
|
 |
 |
1 Kinematische Grundlagen |
Contents / Inhalte Kontinuumsmechanische und rheologische Grundlagen mit einer Einführung in die Tensoranalysis Reynolds-Transporttheorem sowie Beschreibung reibungsbehafteter und reibungsfreier Strömungen Beschreibung von Couette- und Poiseuille-Strömungen mit der kartesischen Form der Navier/Stokes-Gleichung Strömungen mit freien Oberflächen, Fließende und schießende Strömungen, Adhäsion und Kapillarität Strömungsmodellierung in polaren Koordinatensystemen, Hagen-Poiseuille- und Taylor-Couette-Strömung Dimensionsanalyse in der Strömungsmechanik und Einführung in die Grenzschichttheorie an rauhen und technisch glatten Wänden Part B: Applications / Anwendungen Kompressible Strömungen, Bedeutung der Wellengleichung für Doppler-Effekt und Mach'schen Kegel Partikel/Fluid-Interaktion mit Magnus- und Saffmann-Kraft / Basset-Boussinesq-Oseen-Gleichung 2-Weg- und 4-Weg-Kopplung suspensierter Partikel mit Partikel/Wand-Interaktion Geltungsbereich Helmholtz'scher Wirbelsätze Stromfunktionen und komplexe Geschwindigkeitspotentiale, Blasius-Theorem Konforme Abbildungen und die Kutta-Joukowski-Transformation Magnetohydrodynamik von Ferrofluiden bei Raumfahrtanwendungen |
 |
 |
Learning Objectives / Lernziele Studierende beherrschen Beschreibung und Vorhersage des Verhaltens von Rohr- und Kanal- und Ringspalt-Strömungen. Studierende können die Rauhigkeit von Wänden charakterisieren und die technische Bedeutung für das Strömungsverhalten vorhersagen. Studierende sind in der Lage beliebige Transportgleichungen zu entdimensionieren, um skalenunabhängige Vorhersagen zum Strömungsverhalten treffen zu können. Studierende können das Verhalten kompressibler Stömungen im transienten sowie im Überschallbereich vorhersagen. Studierende das Verhalten Partikelsuspension variierender Größe und Partikeldichte charakterisieren. Studierende können den Einfluss magnetischer Felder auf das Fließverhalten elektrisch leitender Fluide vorhersagen (Ferrofluide). |
 |
 |
|
Thermo-Fluid DynamicsProf. Dr.-Ing. R. Groll
Original title: Thermo-Fluid Dynamics (VAK N.N.) |
 |
|||
 |
|
 |
 |
1 Zustandsgleichungen |
Contents / Inhalte Dimensionsanalyse und Entdimensionierung Auftrieb und natürliche Konvektion Entropiefunktionen und Kreisprozesse Abbrandmechanismen und -geschwindigkeit Verdampfung und Verdunstung Isentrope Überschallströmungen Senkrechter und Schräger Verdichtungsstoß Molekülbewegung idealer und realer Gase Molekülkollision und -diffusion Geschwindigkeitsschlupf in Mikrokanälen Boltzmann-Geschwindigkeitsverteilung Euler-Gleichungen im Phasenraum Ionisationsenergie Potentialabfall und Diffusion ionisierter Gase Ionentemperatur und Ionisationsgrad schwach geladener Plasmen |
 |
 |
Learning Objectives / Lernziele Studierende verstehen die erzwungene und natürliche Konvektion in Wärmetauschern. Studierende können den Phasenübergang zur Auslegung von Kühlungsmechanismen nutzen. Studierende können Energieumwandlung in Gasturbinen und Wärmepumpen quantitativ bestimmen. Studierende können Eigenschaften von Überschallströmungen für die Entwicklung von Triebwerken oder Wiedereintrittssystemen nutzen. Studierende können die Dynamik molekularer Gasströmungen in Mikrokanälen beschreiben. Studierende verstehen die verallgemeinerte Modellierung der Dynamik verdünnter Gase. Studierende verstehen den Zusammenhang der Dynamik von Ladungsträgern mit elektrischer Plasmaentladung. |
 |
 |
|
Modelling Turbulent FlowProf. Dr.-Ing. R. Groll
Original title: Modellierung turbulenter Strömungen (VAK 04-326-LuR-007) |
 |
|||
 |
|
 |
 |
1 Statistische Strömungsmechanik |
Contents / Inhalte Statistische Beschreibung turbulenter Strömungen, Reynolds- und Favre-Mittelung Mischungswegmodell, turbulente Längen und Geschwindigkeiten Numerische Modellierung turbulenter Kanalströmungen Randbedingungen zur Berechnung der mittleren Geschwindigkeit Räumliche und zeitliche Auflösung bei der Simulation instationärer Strömungen Homogene Turbulenz und Gleichgewichtsturbulenz Wirbelviskositätsmodelle wie k-ε- und k-ω-Modell Dämpfungsfunktionen und Low-Reynolds-Modelle Energiekaskade und Direkte numerische Simulation (DNS) und Finite-Volumen-Methoden Large-Eddy-Simulation und Druck-Korrekturverfahren Kompressible Turbulenzmodellierung Anisotrope Reynolds-Spannungsmodellierung Druck-Scherkorrelation und turbulenter Transport Bedeutung der Hauptinvarianten für die Anisotropiecharakterisierung turbulenter Strömungen |
 |
 |
Learning Objectives / Lernziele Studierende verstehen die Bedeutung turbulenter Diffusion sowie den Ansatz unterschiedlicher Wirbelviskositätsmodelle Studierende verstehen die Programmierung einfacher, instationärer, numerischer Solver für turbulente Kanalströmungen mit verschiedenen Turbulenzmodellen Studierende können Wandgrenzschichtmodelle sowie Turbulenzmodelle numerisch anwenden, bei denen die Wandgrenzschicht numerisch aufgelöst wird Studierende verstehen die Bedeutung unterschiedlicher, Turbulenz charakterisierender Skalenbereiche sowie die Bedeutung der Reynoldszahl für deren Aufweitung Studierende können numerische Gitter für Large/Eddy-Simulationen und direkte numerische Simulationen entwickeln Studierende können anhand der zeitlichen Entwicklung der Hauptinvarianten den Grad anisotroper Turbulenz bestimmen |
 |